Lathe
Lathe operations encompass a range of machining techniques conducted on a lathe machine, a versatile tool used for shaping, cutting, drilling, and turning various materials like metal, wood, and plastics. These operations include turning, which produces cylindrical shapes, facing for flat surfaces, and taper turning for tapered shapes. Lathes are fundamental in manufacturing and machining processes, offering precision and flexibility in crafting a wide array of components and products.
Lathe Safety
A lathe is a dangerous piece of industrial equipment and safety must be considered durring operation.
The dangers include:
-
Risk of Entaglement
A major risk in lathe operations is being pulled into the machine.
This may casue serious lacerations, frictions burns, broken bones, and death.
This is generaly caused by loose clothing, hair, or jewelry.
Confirm all hoodie strings are tucked inside your hoodie and will not come free. -
High Roataional Energy
A moderate risk in lathe operations is being struck by a rotating object.
This can casue lacerations and broken bones.
This is generaly caused by contact with the chuck, leaving the chuck key in the chuck, or by improperly securing the work piece.
To reduce the risk of harm, work slowly and think through your actions and placment of your hands durring operation. -
Flying Debris
A minor risk in lathe operations is being struck by debris.
This debris can be metal shavings, objects that have been parted off, or shattered tooling.
This can cause minor lacerations and eye injury.
To reduce the risk of harm, always wear saftey glasses while in proximity of an operational lathe, and place you body to the side or the object you are parting off. -
Sharp Edges
A minor risk in lathe operations in being cut by sharp edges.
Objects like metal shavings, cutting surfaces, and machined edges have sharp edges.
This can cause minor lacerations.
To avoid being hurt do not handle metal shavings with bare hands, utilize cleaning tools and gloves.
To adoid being hurt machined parts should be sanded/filed to remove sharp edges. This can be acomplished on the lathe or any other piece of grinding equipment.noteGloves should never be worn durring lathe operation due to risk of entanglement.
Lathe Operation
workpiece setup
Tool setup
machining
HUD operation Clean up
Workpiece Setup
The workpiece or stock is the material that will be turning.
To properly clamp or chuck the material make sure the 3 teeth of the chuck are fully engaged with the
qw=
Material Supports (Optional)
Addition support should be used to brace longer stock, or to keep stock stable durring precise or aggressive turning operation.
Extra support can be added by center drilling a hole into the end of the stock
Tool Selection
Common Operations
Durring the manufacturing of the robot,
Straight Turning
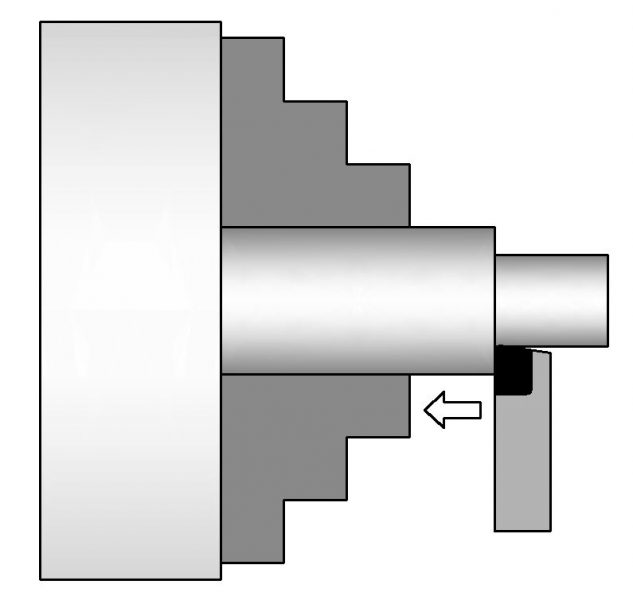
Turning is used to remove material to change the diameter or surface finish of a workpiece.
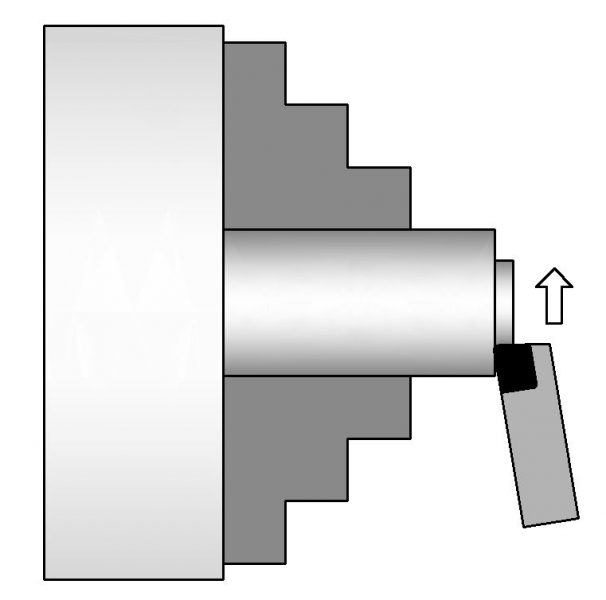
Facing
Parting
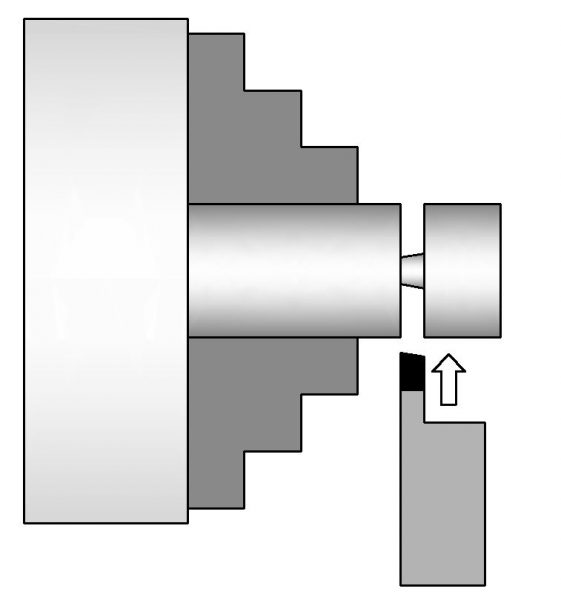
Parting is used to cut off a finished part from the remaining stock material.
Drilling
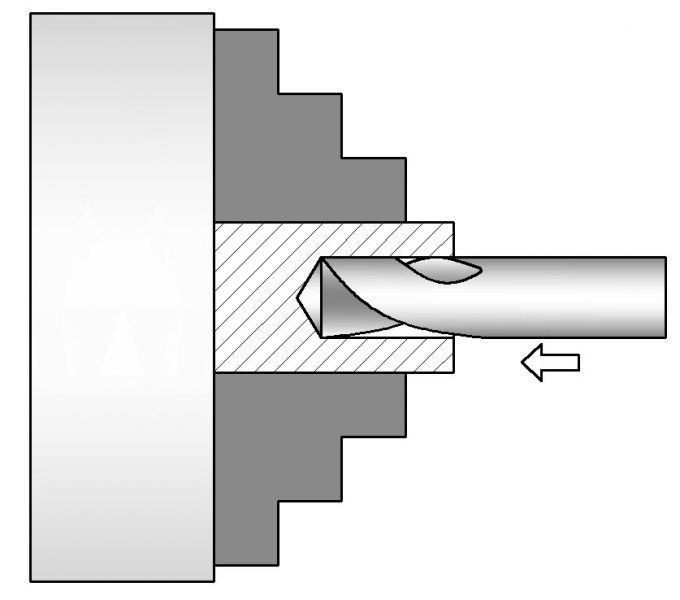
Drilling involves Drilling is used to
Center Drilling
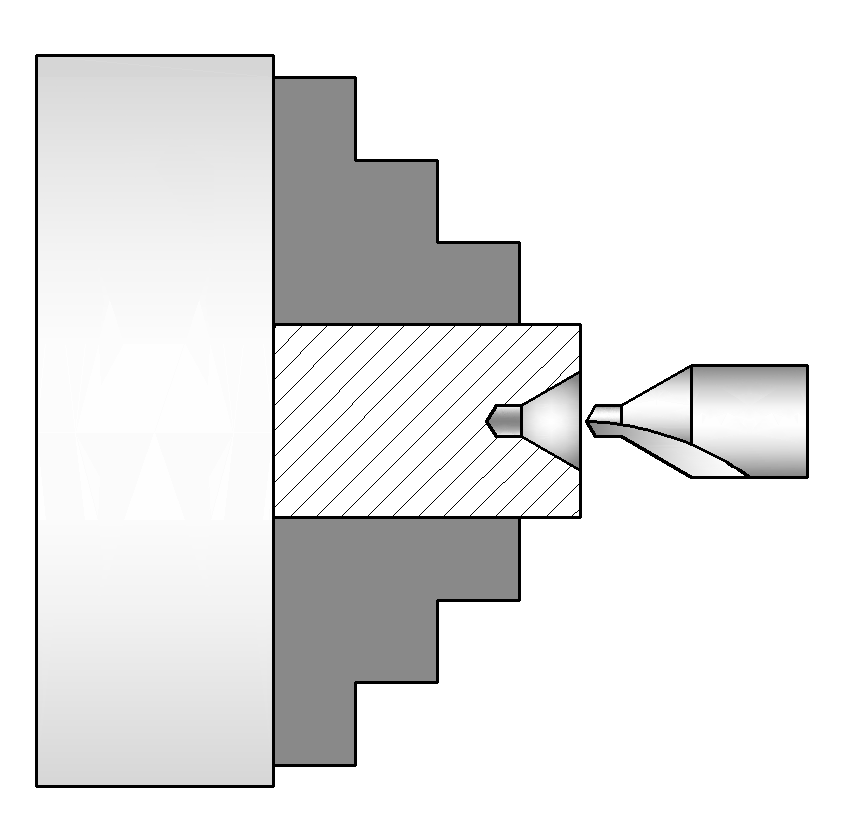
Sanding
Rare Operations
The following operations are rarely utilized in our manufacturing process.
They are however utilized heavily in manufacturing.
Taper Turning
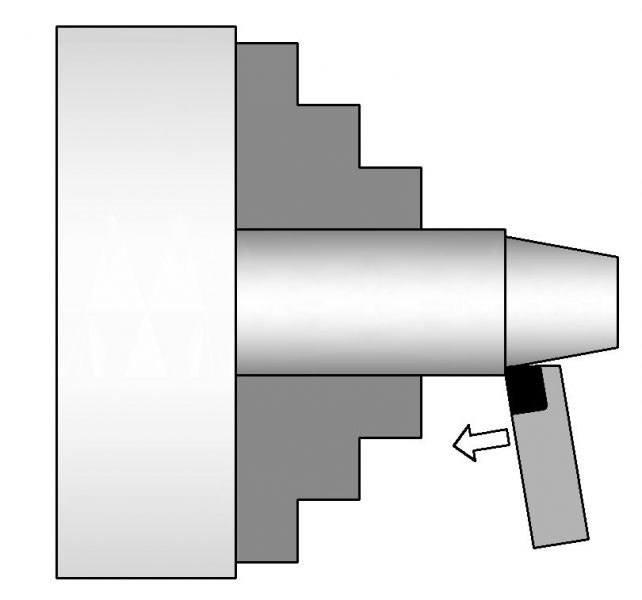
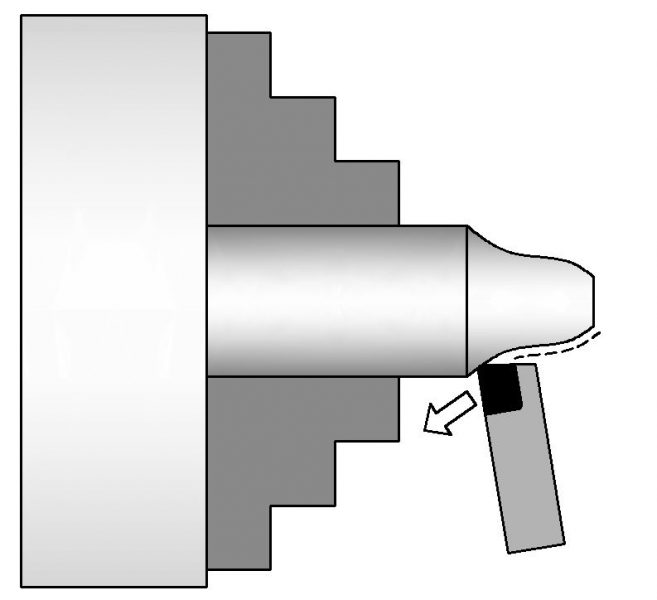
Contour Turning
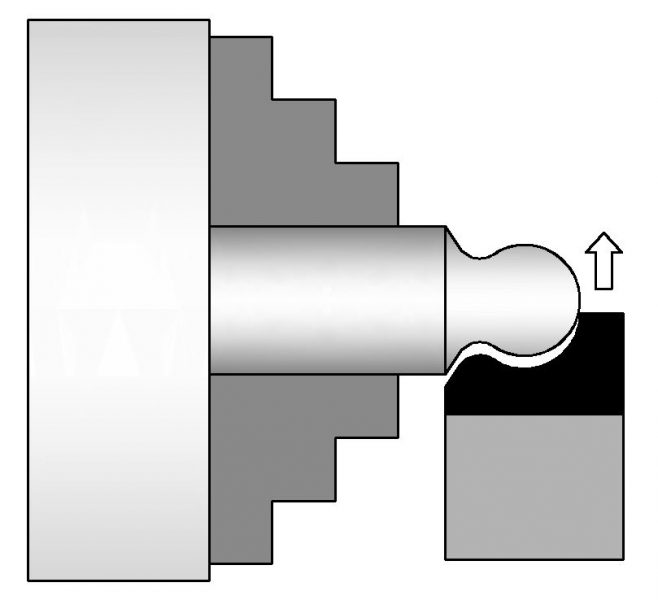
Form Turning
Boring
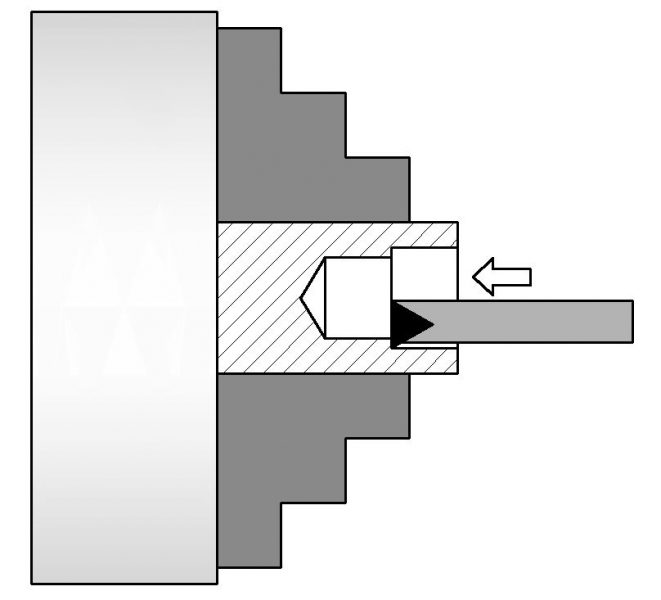
Boring is used to increase the the internal diameter (ID) of a workpeice.
Boring cannot make a new hole, only expand it.
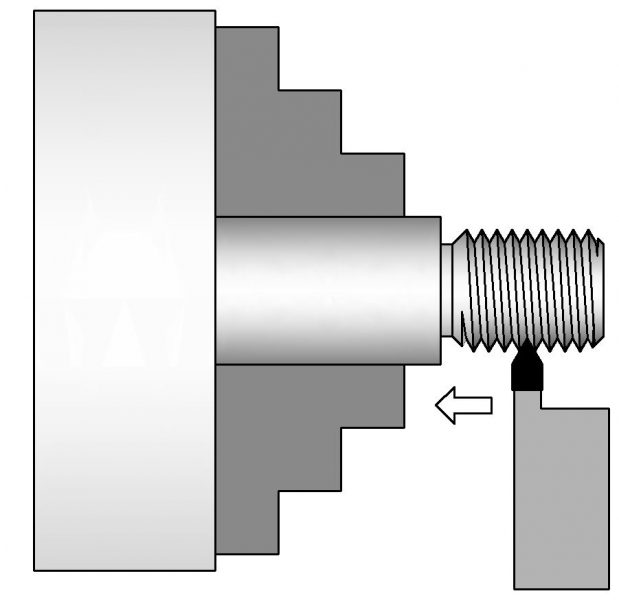
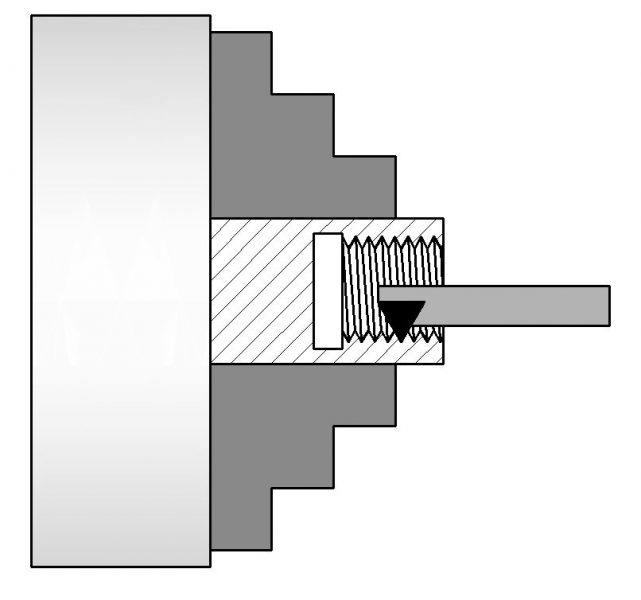
Threading
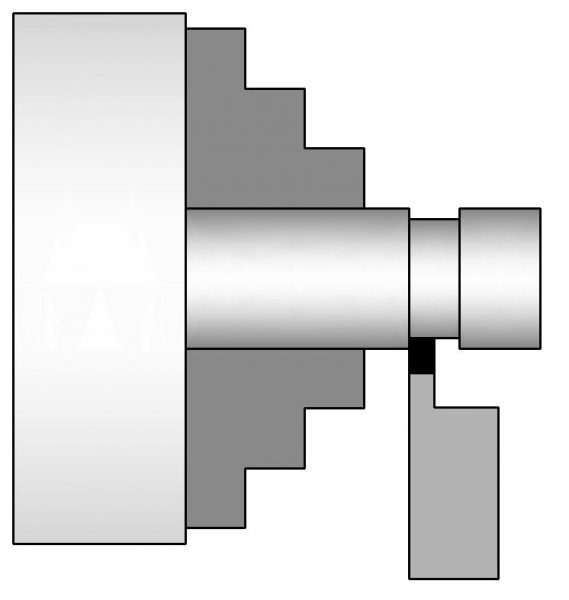
Grooving
Knurling
Tool setup
Refrences
Engineering Technology
Robert Hewitt
Source: EngineeringTechnology.org
License: CC BY 4.0 License.